BWR reactor
A boiling water reactor uses Light WaterLight WaterLight water, although appearing to have a fancy name, is literally just ordinary water....except it does contain a small amount of Heavy Water. The point of light water is that it can be used as a moderator --however it can only be used in certain situations, as it absorbs too many neutrons to be used with unenriched uranium (which is why light water is presumably used in Spent Fuel Pools) Light water is mainly used in BWR reactors & PWR reactors Uranium Enrichment is necessary for the usage of as both coolant and neutron moderator. The second most used reactor, next to the PWR reactorPWR reactorThis reactor is a PWR reactor - a pressurized water reactor. This is a specific type of Nuclear Reactor--in that it is pressurized water. This is also the most common type of reactor used and produced. The fuel rods are pressurized with helium, and the fission gas products result in more stability; as fuel "burns" in the reactor, the density increases resulting in small voids developing. Helium pressurization is necessary as these voids can cause potential rupture of fuel rods. Furthermore, thes, there are approximately 75 plants in current operation. The efficiency of these reactors is about 46%, with 33-34% in practice. Enriched uranium is used as nuclear fuel, as light water absorbs too many neutrons to use UraniumUraniumUranium is a naturally occuring element - atomic number of 92 and in the actinides group. Uranium is radioactive - decaying over time and releasing energy. This is the reason why Uranium is the primary source of fuel for Nuclear Reactors. The amount of energy in a single gram of uranium is about 3.5-4.5 tons of coal; around 702 gigajoules - whilst each gram of coal has around .0293 gigajoles of energy; a staggering amount inside of uranium. Isotopes There are three natural isotopes of uranium that is natural. Light water is not as good of a moderator compared to Heavy WaterHeavy WaterHeavy Water is literally Deuterium oxide. It's molecular formula is that of regular Light Water--H2O, however it contains two atoms of deuterium and one atom of Hydrogen; resulting in 2D2O. It is about 10.6% denser than tap water and has a higher melting point, tasting slightly sweeter and can affect bioloigcal systems; large amounts are needed to poison humans, although it is toxic. It is produced using the Girdler sulfide process, and the usages of Heavy Water is mainly for nuclear science; or graphite, but it is good as in the event of a LOCALOCALoss of Cooling Accident - inside of Nuclear Reactors, this is the official term for if there is a loss of coolant used to cool the reactor. \#stub or steam overflow, moderation with stop resulting in the chain reaction ceasing.
Operation
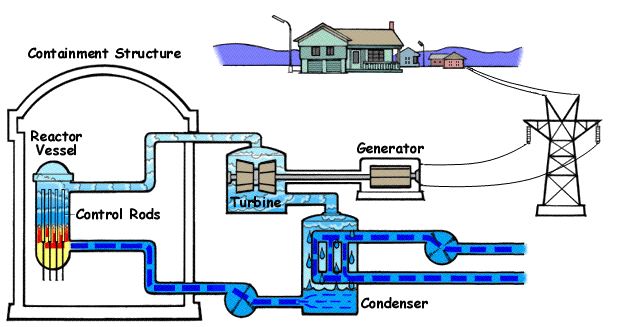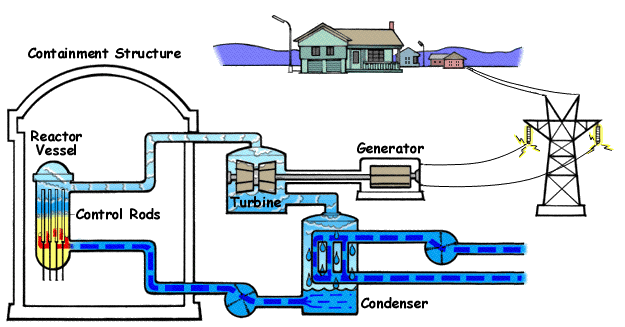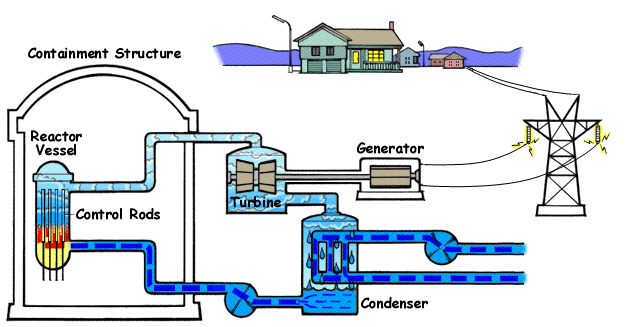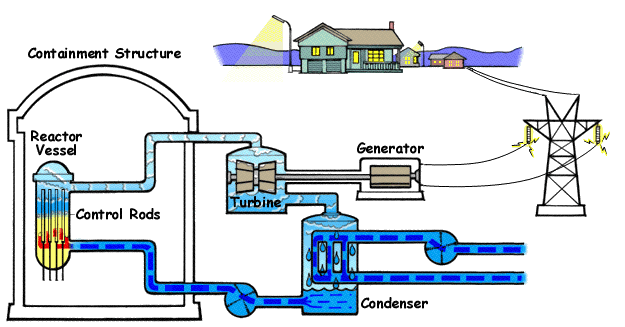
In a BWR reactor, water is circulated through the reactor vessel, and through the core it turns into steam. After passing through steam dryers and separator assemblies, this steam directly pipes into the high pressure and low pressure steam turbines, generating electricity. Afterward, this steam is passed through a CondenserCondenserA steam condenser is a common system used to turn input steam into water again. When steam is heated inside of a facility, such as a coal firing plant, Nuclear Reactor, or other system, it is pressurized then run through high pressure and low pressure turbines, eventually reaching the end of the path where it is still hot yet needs to be cycled back into water; as you must recycle it to reheat it again. For this reason, a steam condenser unit must be used. How does a condenser work? Savree Expl, that condenses steam back into water. The condenser can use either a natural water source nearby or cooling towers. BWRs operate at high pressures, as the water can remain in liquid form at higher temperatures (similar to how a PWR works, however that is the unintended result). Since pressure in BWRs are lower then PWRs, the specific power is less, and the BWR must be larger to provide the same power.
Cooling Safety
Since there is only one primary loop, water that is in the RPV goes directly to the turbines. Therefore, less water needs to flow through a BWR compared to a PWR, however, if there is a leak, the water is highly radioactive, Therefore, even non-reactor parts of the plant must be highly shielded against incidents.
Control rod placement
Control rods are placed in the bottom of the reactor, rather then the top, as the top is taken up by the steam dryer, steam separator, etc. There is a higher reactivity of the fuel due to its moderation, and control rods are needed to change reactivity as necessary. Control rods are controlled by the Control Rod DriveControl Rod DriveThe CRD system in a Nuclear Reactor is crucial for its operation. The CRD is necessary for the percise control of Control Rods in a reactor. In BWR reactors, this is especially necessary, as control rods are inserted via the bottom penetration points in the RPV, and if there is a SCRAM, gravity cannot be relied on to insert the rods, differing from other reactor designs. Therefore, a method to SCRAM the plant and percisely control the rods in a BWR is necessary. BWR Control Rod Drive Mechanisms system.
Emergency Operations
In an emergency, the ECCSECCSEmergency Core Cooling Systems encompass all of the emergency systems used in Nuclear Reactors. Inside of the RPV of a reactor is the reactor core, which gets hot due to fission during operation. In the event that primary cooling systems go offline due to a powerloss, LOCA, or other reason, ECCS systems are automatically enabled. ECCS broadly describes all of the emergency systems used, however specific emergency systems can be used in isolation. Some ECCS systems are specified for a specific d will activate. BWR plants, like other reactors, have emergency diesel generators that can be used for the operation of essential systems if there is a loss of outside power or LOOP event. Furthermore, there are systems that don't require any power or control to activate that are listed in the ECCS.
See Reactor ManualsReactor ManualsDuring the course of my research into Nuclear Reactors, I am using NRC provided documents often to check my information and learn more about the inner workings of reactors. Fortunately, the NRC publicly posts these manuals at the following link: https://www.nrc.gov/reactors/operating/licensing/techspecs/current-approved-sts.html |Technical Specification Publication Title|Volume| |-----------------------------------------|------| |Babcock and Wilcox Plants, Rev. 5 STS (NUREG-1430), Vol. 1, Spec for more info on where I am getting this information.
BWR Plant Layout
In a BWR plant, there are many different buildings containing the structures for the reactor.
Containment Building
This building has the RCS, Drywell, Suppression Pool, Upper Pool, alongside systems
Turbine Building
Contains turbine and all equipment and auxiliary equipment
Auxiliary Building
Contains safety systems, fuel storage and shipping
Control Building
Houses MCR, and control + electrical systems
Diesel Generation Building
This hosts the diesel generators and emergency supplies
Radwaste Building
This houses systems to process radioactive substances made by the plant
Intake Building
Houses equipment that provides for heat management of the plant.