VVER Reactor (WWER)
Water-Water energetic reactor (WWER) or the Russian VVER from (from Russian: водо-водяной энергетический реактор, romanized: vodo-vodyanoi enyergeticheskiy reaktor, lit. 'water-water power reactor') is a series of PWR reactorPWR reactorThis reactor is a PWR reactor - a pressurized water reactor. This is a specific type of Nuclear Reactor--in that it is pressurized water. This is also the most common type of reactor used and produced. The fuel rods are pressurized with helium, and the fission gas products result in more stability; as fuel "burns" in the reactor, the density increases resulting in small voids developing. Helium pressurization is necessary as these voids can cause potential rupture of fuel rods. Furthermore, the designs developed originally by the Soviet Union, and now RussiaRussiaLocated in the north-eastern hemisphere of the world, Texas can fit inside Russia 25 times. Russia is the largest country in the world. Known for their vodka, Chernobyl, and the Russo-Ukraine war., by OKB Gidropress.
One of the initial reactor designs other then the RBMK ReactorRBMK Reactor\#stub It is a soviet designed nuclear reactor that uses enriched uranium, with graphite as a moderator, and Light Water as a coolant., this design is a Thermal ReactorThermal ReactorA thermal reactor describes a Nuclear Reactor with the main function of producing thermal heat to be converted to electricity. This term describes all of the operating reactors today with the exception of Fast Neutron Reactors. A thermal reactor is one in which neutrons are necessary to sustain a fissile reaction that creates heat: unlike a FNR that has an excess of neutrons. A thermal reactor specifically uses thermal neutrons - that are slower then fast neutrons. Thermal neutrons ahve the ben design using control rods and Light WaterLight WaterLight water, although appearing to have a fancy name, is literally just ordinary water....except it does contain a small amount of Heavy Water. The point of light water is that it can be used as a moderator --however it can only be used in certain situations, as it absorbs too many neutrons to be used with unenriched uranium (which is why light water is presumably used in Spent Fuel Pools) Light water is mainly used in BWR reactors & PWR reactors Uranium Enrichment is necessary for the usage of coolant. Their power varies, with electric power varying from 210-1300 MW and raw thermal power from 760-3300 MW.
Design
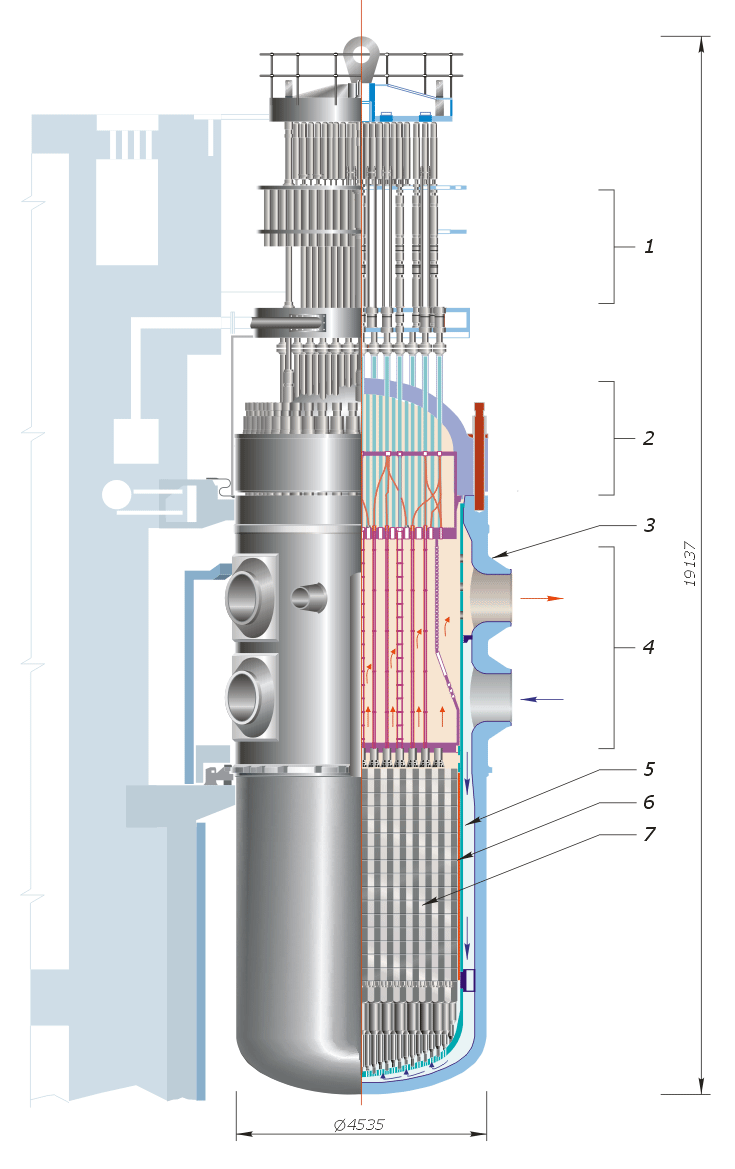
- Control Rod DriveControl Rod DriveThe CRD system in a Nuclear Reactor is crucial for its operation. The CRD is necessary for the percise control of Control Rods in a reactor. In BWR reactors, this is especially necessary, as control rods are inserted via the bottom penetration points in the RPV, and if there is a SCRAM, gravity cannot be relied on to insert the rods, differing from other reactor designs. Therefore, a method to SCRAM the plant and percisely control the rods in a BWR is necessary. BWR Control Rod Drive Mechanisms
- Vessel Head
- RPVRPVReactor Pressure Vessel - contains all of the reactor heat. In BWR reactors, the RPV contains the reactor core - basically the entirety of the main reactor assembly. The RPV is designed to withstand a very large amount of force considering that in a BWR it must withstand the pressure that both it operates at and at emergency designs -- this is due to the fact that in most designs, the RPV isn't considered to be at major risk: even during a major LOCA the RPV is considered to be at healthy condi
- Inlet/Outlet Nozzles
- Core Shroud
- Reactor Core
- Fuel Rods
VVER stands for water-water energy reactor - type of PWR. The distinguishing factor of the VVER is
- Horizontal steam generation
- hexagonal fuel assemblies
- no bottom penetrations in RPV
- High-capacity pressurizers providing a large amount of reactor coolant inventory
Fuel rods are fully immersed at water kept at a high pressure, which is very similar to PWR reactor designs, enabling water to be at a high temperature without boiling. Water serves as both a coolant and a moderator, similar to both BWR and PWR designs. This reactor, specifically, has a Negative Void Coefficient, meaning if water circulation fails, the moderation of the water diminishes and results in reducing reactor intensity. Fuel is lowly enriched, and uses uranium dioxide pellets.
Reactivity is controlled by control rods, with gravity feeding for SCRAMs.
Primary Cooling Circuit
As is a PWR design, the primary circuit is basically water through the RPV, pressurizer, steam gen, then a pump.
Secondary Cooling Circuit
The secondary is the steam gen, turbine, CondenserCondenserA steam condenser is a common system used to turn input steam into water again. When steam is heated inside of a facility, such as a coal firing plant, Nuclear Reactor, or other system, it is pressurized then run through high pressure and low pressure turbines, eventually reaching the end of the path where it is still hot yet needs to be cycled back into water; as you must recycle it to reheat it again. For this reason, a steam condenser unit must be used. How does a condenser work? Savree Expl, deaerator, and then another pump.
Third cooling circuit
Interestingly, there can be another cooling circuit, for industrial and residential heating applications - transferring waste head into the environment from the generation circuit.